Sponsored by KANO & STEM

Team & Project Type
Project Scope
Focus Areas
Tools
Break Down the System
Navigating
INPUT
GNSS data
OUTPUT
Vibration Pattern
Interacting
INPUT
Motion Data
OUTPUT
Digital Features
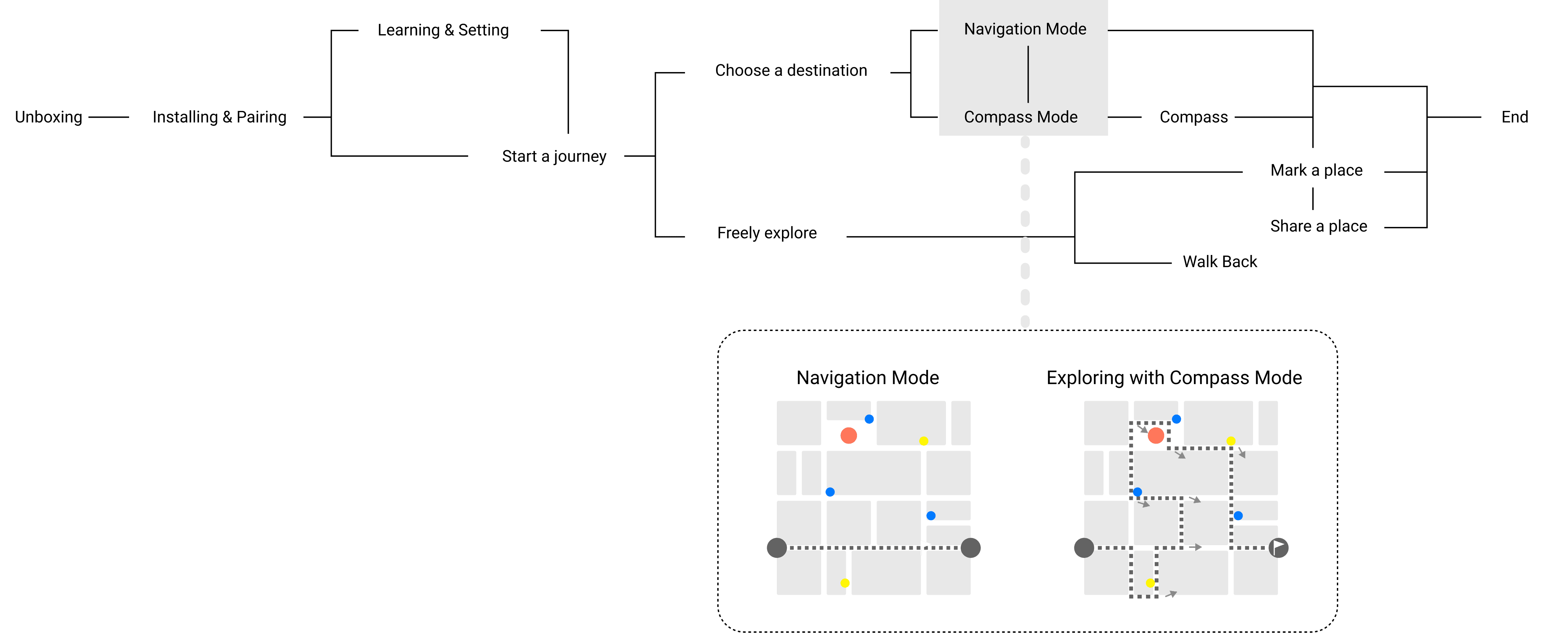
UrbanQuest innovates with a Compass Mode where users’ shoes indicate the direction, like a compass. It encourages users to choose their own paths and explore the city freely.
Lifestyle: Urban enthusiast
Travel: Adventure seeker
Personality: Curious, adventurous
Social: Sociable, community-oriented
Urban Area
Daily Commuting
Travelling
The vibration feedback in the sole provides navigation information, and dynamic capture technology identifies the user’s foot gestures for interaction.
According to recent studies, Gen Z averages up to 9 hours per day on digital devices.
An observational study has found that around 20 per cent of pedestrians in Melbourne are distracted by smartphones.
A study shows that nearly half of teens are online almost constantly, leading to a sense of disconnection from real-life interactions.
Digital Map? Not enough!
Research
Key Insight
Google Maps focuses on efficiency, but not experience.
Map apps rely heavily on visuals, overlooking other sensory potentials.
Users rarely explore area outside of suggested routes.
Can we go beyond digital maps?
“The physical act of moving your arm and feeling the paper under your finger gives your brain haptic and sensorimotor cues that contribute to the formation and retention of the cognitive map.”
“Why Paper Maps Still Matter in the Digital Age”
The MIT Press
February 5, 2019


Stanford researchers have developed a self-navigating smart cane for the visually impaired, featuring a motorized wheel at the tip that provides real-time feedback.
Equipped with sensors like GPS, accelerometers, magnetometers, and gyroscopes, it tracks location, speed, and direction.

The Ashirase navigation system for the visually impaired uses a smartphone app and a 3D vibration device with a motion sensor, attached inside the shoe.
It provides navigation via foot vibrations, guided by GNSS positioning and motion data.
We need an alternative way of navigating that allows people to move their body and keep real-life interactions with the city.
These two precedents demonstrate the technical feasibility of creating alternative ways of navigating.
Smart footwear integrated with a digital navigation system that enhances the urban experience.
Interaction + Device + Platform
The way it communicate...
How to make interaction more intuitive?
Workshop: Make Your Shoes
“Make Your Shoes” workshop explores foot gestures as a medium for intuitive interaction. I recruited participants from diverse backgrounds to ensure the gestures were intuitive across cultures. They were asked to create shoes and test gestures based on various prompts.
It is not only a footwear device, but also a foot-gesture interface.

Pairing

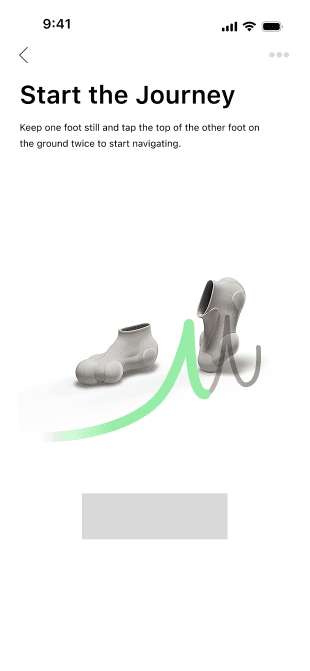
Start the journey

End the journey

Switch Modes

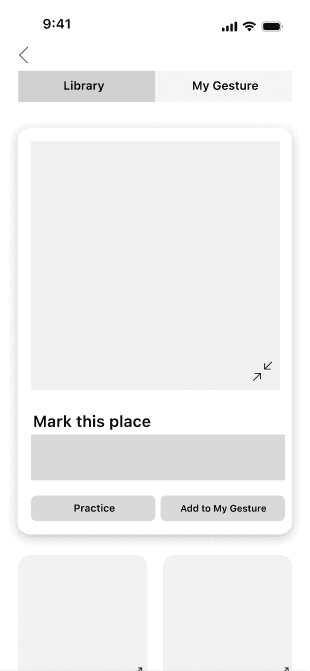
Mark this place

Random

Share the location

Hello!
Engineering Feedback
Iteration
To create a more intuitive user experience, I have decided to adopt this charging method.

I adopted a modular design with Kano color schemes for a more pleasant assembly and disassembly experience.



Headline
Roboto Bold 28
Headline
Roboto Regular 28
Title
Roboto Regular 22
body
Roboto Regular 14
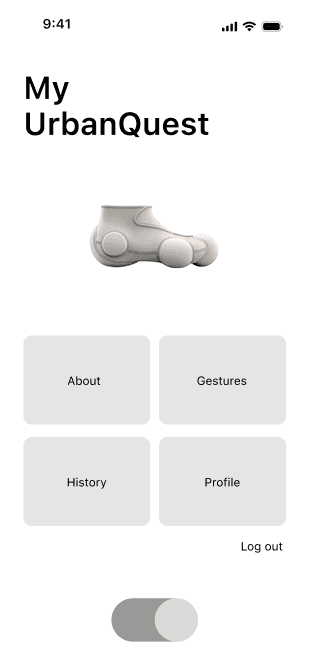
Device Management
As an app tightly integrated with wearable devices, this page is dedicated to managing device settings and usage configurations. Users can check connection status and battery level, or enter the gesture library to customize gesture commands based on their usage habits.
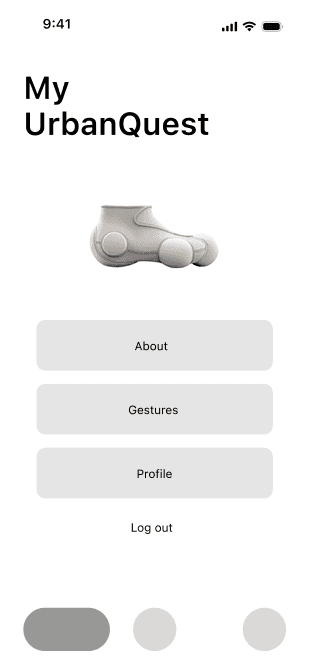
Gesture Library
On this page, users can manage the interaction commands and corresponding foot gestures they want to use. After learning a new gesture, users can add it to their personal gesture library for quick access in everyday use.
Gesture Learning
Users can learn new gesture commands on this page. Guided by on-screen animations and supported by motion sensors in the wearable device, users can practice in real time and receive immediate feedback.
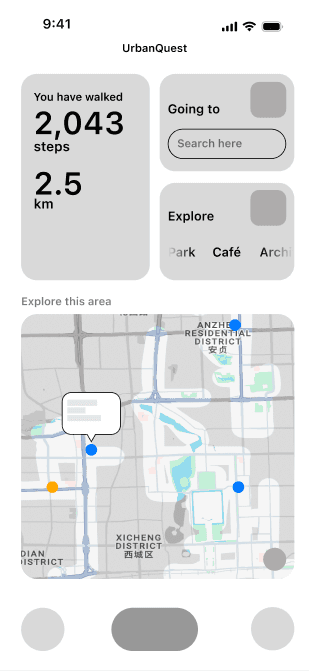
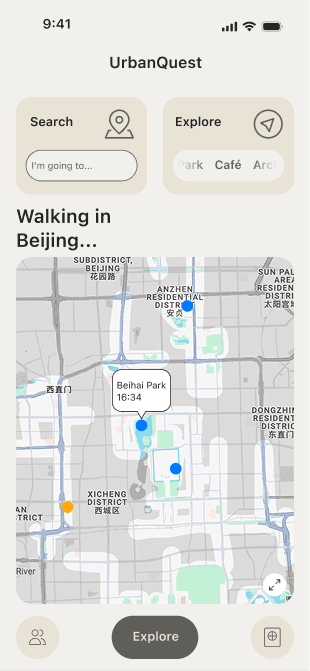
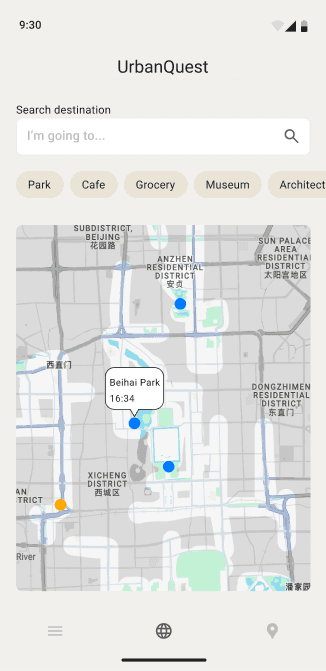
Exploration Portal
Here, users can visually explore unlocked city streets on the map or choose to explore nearby destinations. The goal is to encourage active urban exploration and help users discover hidden gems within the city.